Thyroid in Women: Your Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Thyroid Health
Introduction to Thyroid Health
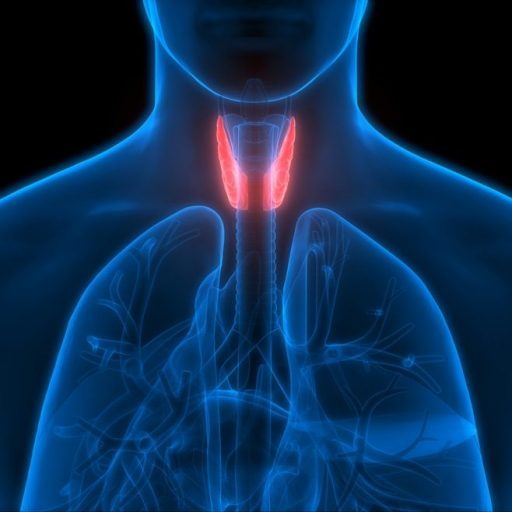
The Critical Role of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid, a small yet powerful butterfly-shaped gland, plays a pivotal role in regulating vital body functions. It’s essential for metabolism, temperature control, and overall well-being. Understanding its functions is the first step in recognizing thyroid-related health issues.
Prevalence of Thyroid Disorders in Women
Thyroid disorders are a significant health concern, especially for women. Studies show that one in eight women will face a thyroid issue in her lifetime. This website aims to provide comprehensive insights into thyroid health, combining medical research with personal experiences.
Thyroid disorders in women are not just medical conditions; they are intricately linked with various stages of a woman’s life, affecting her health, mood, energy levels, and even interpersonal relationships. The complexity of thyroid hormones and their impact on women’s health cannot be overstated. For instance, during pregnancy, thyroid disorders can not only affect the mother’s health but also have a profound impact on fetal development and the child’s future health. Similarly, during menopause, changes in thyroid function can mimic or exacerbate menopausal symptoms, making diagnosis and treatment a delicate balancing act. Understanding these intricate connections is crucial for effective management and overall well-being.
In the landscape of online resources about thyroid disorders, ‘Thyroid in Women’ stands out for its unique blend of professional medical insights and real-life experiences. Unlike many other resources that primarily focus on the medical aspects, our website delves into the personal impact of thyroid disorders on women’s lives, offering a holistic view. Here’s how ‘Thyroid in Women’ compares with other leading resources:
- Depth of Information: While other sites provide basic medical information, ‘Thyroid in Women’ offers a more comprehensive understanding, covering everything from symptoms to lifestyle management.
- Personal Insights: Our content is enriched with personal stories and experiences, making it more relatable and supportive for women dealing with thyroid issues.
- Interactive Tools: The interactive symptom tracker and personalized recommendations offer practical support, a feature often missing in other resources.
- Focus on Women’s Health: We specifically address how thyroid disorders intersect with different stages of a woman’s life, a perspective that is often underrepresented in general medical resources.
- Up-to-Date Research: Our commitment to providing the latest research and treatment options ensures that our readers have access to the most current information.
By offering these unique features, ‘Thyroid in Women’ not only educates but also empowers women to actively manage their thyroid health.
According to the American Thyroid Association, approximately 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disease, and up to 60 percent of those are unaware of their condition. [Reference: American Thyroid Association, ‘General Information/Press Room’]
In recent years, groundbreaking research has unveiled new approaches to managing thyroid disorders, particularly in women. These include personalized medicine based on genetic profiling, which tailors treatment to individual genetic makeup, and the use of advanced imaging techniques for more precise diagnosis. Additionally, emerging studies on the gut-thyroid axis highlight the significant impact of gut health on thyroid function, opening new avenues for holistic management strategies.
Understanding Thyroid Disorders
Hyperthyroidism: When the Thyroid Overworks
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid produces excess hormones. Symptoms include rapid metabolism, anxiety, and nervousness. It’s a complex condition that requires careful medical management.
Hypothyroidism: The Underactive Thyroid
In contrast, hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones. Symptoms like weight gain, fatigue, and hair loss are common. Autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s disease, are often the cause.
The Spectrum of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid health issues encompass a range of disorders, each with unique causes and symptoms. From iodine deficiency to genetic factors, understanding these nuances is crucial for effective management.
Interactive Thyroid Wellness Tracker
To further empower our readers, we’re introducing an ‘Interactive Thyroid Wellness Tracker.’ This personalized tool allows you to monitor your thyroid health by tracking symptoms, dietary habits, and medication effects over time. It provides actionable insights and alerts you to potential health changes, encouraging proactive management of your thyroid condition.
The Impact of Thyroid Disorders on Women’s Health
Age-Related Thyroid Issues
Thyroid disorders can manifest differently across various life stages. Younger women may experience menstrual irregularities, while older women might face complications post-menopause. Recognizing these age-related differences is key to appropriate care.
Research indicates that women are five to eight times more likely than men to have thyroid problems. [Reference: Vanderpump, M.P., ‘The Epidemiology of Thyroid Disease’, British Medical Bulletin, 2011]
Thyroid Disorders and Pregnancy
Thyroid health is particularly crucial during pregnancy. Disorders can pose risks to both mother and baby, making early detection and management vital for a healthy pregnancy outcome. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists highlights that thyroid diseases can affect both pregnancy and postpartum health. [Reference: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, ‘Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy’, ACOG Practice Bulletin, 2020]
Comprehensive Treatment and Management Strategies
Personalized Treatment Approaches
Treatment for thyroid disorders varies widely, from medication for hormone replacement to lifestyle adjustments. Each individual’s treatment plan should be tailored to their specific needs and symptoms.
Lifestyle and Dietary Adjustments
Diet and lifestyle play a significant role in managing thyroid disorders. Healthy eating, stress reduction, and regular exercise can greatly improve symptoms and enhance quality of life.
To further enhance your understanding, we’re introducing an interactive section where you can track symptoms and potential risk factors for thyroid disorders. This tool will guide you through a series of questions about your health, lifestyle, and family history, offering personalized insights and recommendations. Additionally, we’ve compiled a series of real-life case studies from women who have navigated the challenges of living with thyroid disorders. These stories not only provide relatable experiences but also demonstrate the diverse ways in which these conditions can manifest and be successfully managed.
The Endocrine Society’s clinical practice guidelines provide comprehensive recommendations for the treatment of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. [Reference: Jonklaas, J. et al., ‘Guidelines for the Treatment of Hypothyroidism’, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2014]
Deep Dive: Causes and Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
In-Depth Look at Causes
Understanding the Root Causes of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders can stem from a variety of factors. Understanding these is crucial for both prevention and effective treatment. This section explores the common causes, providing insights into how these factors impact thyroid health.
Autoimmune Diseases: The Body’s Misguided Attack
Autoimmune disorders are a leading cause of thyroid problems. In conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. This attack disrupts normal thyroid function, leading to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Iodine Levels: A Delicate Balance
Iodine, a mineral essential for thyroid hormone production, plays a critical role. Both iodine deficiency and excess can lead to thyroid disorders. While iodine deficiency is more common in developing countries, excess iodine from certain medications or dietary sources can also cause thyroid problems.
Genetic Predisposition: The Hereditary Factor
Genetics can influence the likelihood of developing thyroid disorders. A family history of thyroid issues increases the risk. Understanding your genetic predisposition helps in early detection and management.
Environmental Influences: External Factors
Environmental factors, including exposure to certain chemicals and radiation, can affect thyroid health. For instance, exposure to radiation, especially in childhood, increases the risk of thyroid cancer. Certain chemicals in the environment, like perchlorate, can also disrupt thyroid function.
Hormonal Changes: The Impact of Life Stages
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can trigger thyroid disorders. Pregnancy, menopause, and other life stages involving significant hormonal changes are times when women are particularly susceptible to thyroid issues.
Lifestyle Factors: Diet and Stress
Lifestyle choices, such as diet and stress levels, play a role in thyroid health. A diet low in selenium and zinc, nutrients important for thyroid function, can contribute to problems. Chronic stress is another factor that can disrupt thyroid function.
Comprehensive Symptom Checklist for Thyroid Disorders
This comprehensive checklist covers everything from weight changes and fatigue to mood swings and menstrual irregularities. Early recognition of these signs is crucial for timely and effective treatment. This checklist covers the key symptoms associated with thyroid disorders:
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
- Increased Heart Rate: A rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss despite normal eating habits.
- Increased Appetite: Feeling unusually hungry.
- Nervousness and Anxiety: Experiencing heightened anxiety without a clear cause.
- Tremors: Noticeable trembling in the hands and fingers.
- Excessive Sweating: Increased perspiration not linked to physical activity or temperature.
- Heat Sensitivity: Intolerance to heat and excessive sweating.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired even after adequate rest.
- Difficulty Sleeping: Experiencing insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns.
- Muscle Weakness: Unusual weakness, particularly in the upper arms and thighs.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness, not relieved by rest.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained increase in weight.
- Reduced Appetite: Decreased hunger.
- Cold Sensitivity: Feeling unusually cold.
- Joint and Muscle Pain: Experiencing aches in muscles and joints.
- Constipation: Persistent constipation.
- Dry Skin: Noticeably dry or rough skin.
- Hair Loss: Thinning hair or loss of hair.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness or depression.
- Menstrual Changes: Irregular or heavy menstrual cycles.
General Symptoms Common to Both Conditions
- Goiter: Swelling in the neck due to an enlarged thyroid gland.
- Mood Swings: Rapid and unexplained changes in mood.
- Cognitive Difficulties: Problems with memory or concentration.
- Cholesterol Issues: Unexplained changes in cholesterol levels.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty in sleeping or excessive sleeping.
Note to Readers:
This checklist is a guide and not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Author’s Perspective: Merging Medical Expertise with Personal Experience
Samantha Clarke’s Journey
As a Registered Endocrinology Nurse and a patient of thyroid disorder, I, Samantha Clarke, offer a unique dual perspective. My journey, filled with both clinical knowledge and personal struggles, aims to empower and educate others facing similar challenges.
Bridging the Gap Between Medical Knowledge and Real-Life Experience
My mission is to make complex medical information accessible and actionable. This website translates medical terms into practical advice, providing a holistic understanding of thyroid health.