Hormone deficiency in women is a significant health concern that can affect various aspects of physical and emotional well-being. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for those who may be experiencing hormone imbalances. This guide aims to provide comprehensive and trustworthy information on hormone deficiency in women, aligning with the highest standards of content quality and reliability.
Understanding Hormones and Their Role
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by the endocrine glands in the body. They travel through the bloodstream to tissues and organs, playing a vital role in regulating many bodily processes, including:
- Growth and development
- Metabolism
- Sexual function
- Reproduction
- Mood regulation
Key Hormones in Women
- Estrogen: Crucial for sexual and reproductive development.
- Progesterone: Plays a role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
- Testosterone: Affects bone density, muscle strength, and sex drive.
- Thyroid Hormones: Regulate metabolism, energy, and mood.
- Cortisol: The stress hormone, which also affects metabolism.
Symptoms of Hormone Deficiency
Hormone deficiencies can manifest in various ways, depending on which hormone is imbalanced. Common symptoms include:
- Menstrual Irregularities: Skipped periods or irregular cycles.
- Mood Swings and Depression: Unexplained emotional changes.
- Weight Gain: Especially around the abdomen, despite diet and exercise.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness not relieved by rest.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Low Libido: Decreased interest in sexual activity.
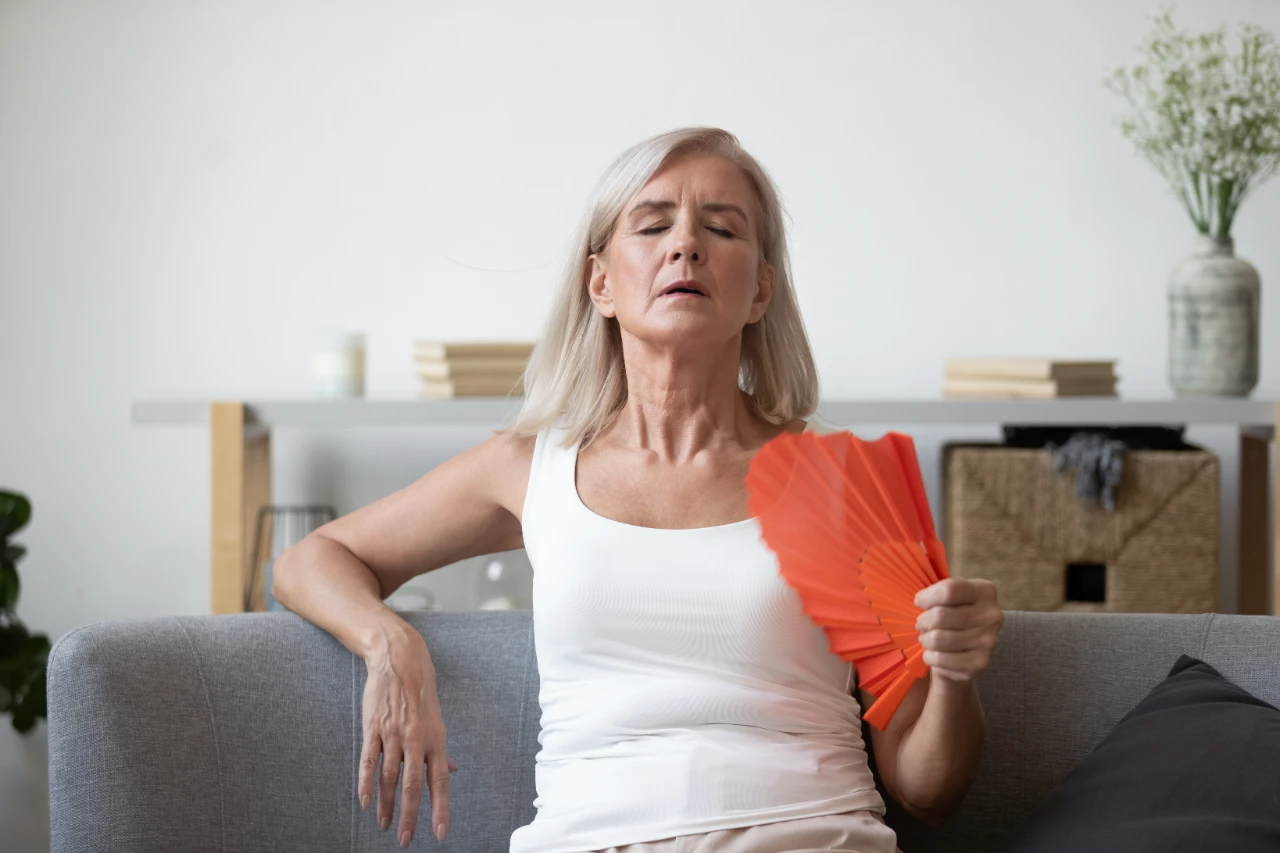
- Hot Flashes and Night Sweats: Common during menopause.
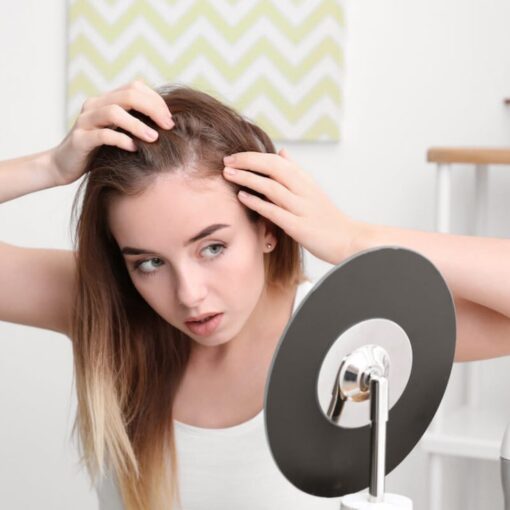
- Skin and Hair Changes: Dry skin, hair loss, or thinning.
- Memory Fog: Difficulty concentrating or remembering things.
Causes of Hormone Deficiency
Several factors can contribute to hormone imbalances in women:
- Age: Natural changes during menopause.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress.
- Medical Conditions: Thyroid disorders, PCOS, and others.
- Medications: Certain drugs can affect hormone levels.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to endocrine disruptors.
Diagnosing Hormone Deficiency
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History Review: Discussing symptoms and health history.
- Physical Examination: Checking for physical signs of hormone imbalance.
- Blood Tests: Measuring levels of various hormones.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the specific hormone deficiency and may include:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Supplements deficient hormones.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet, exercise, and stress management.
- Medications: To address specific symptoms or related conditions.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, herbal supplements (consult a healthcare provider before starting).
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
- Balanced Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: At least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days.
- Stress Reduction: Yoga, meditation, and other relaxation techniques.
- Adequate Sleep: 7-9 hours per night.
- Avoiding Toxins: Limit exposure to pesticides, plastics, and other endocrine disruptors.
Conclusion
Hormone deficiency in women is a complex issue that requires a nuanced understanding of symptoms, causes, and treatment options. By recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate medical care, women can effectively manage hormone imbalances and maintain their overall health and well-being.